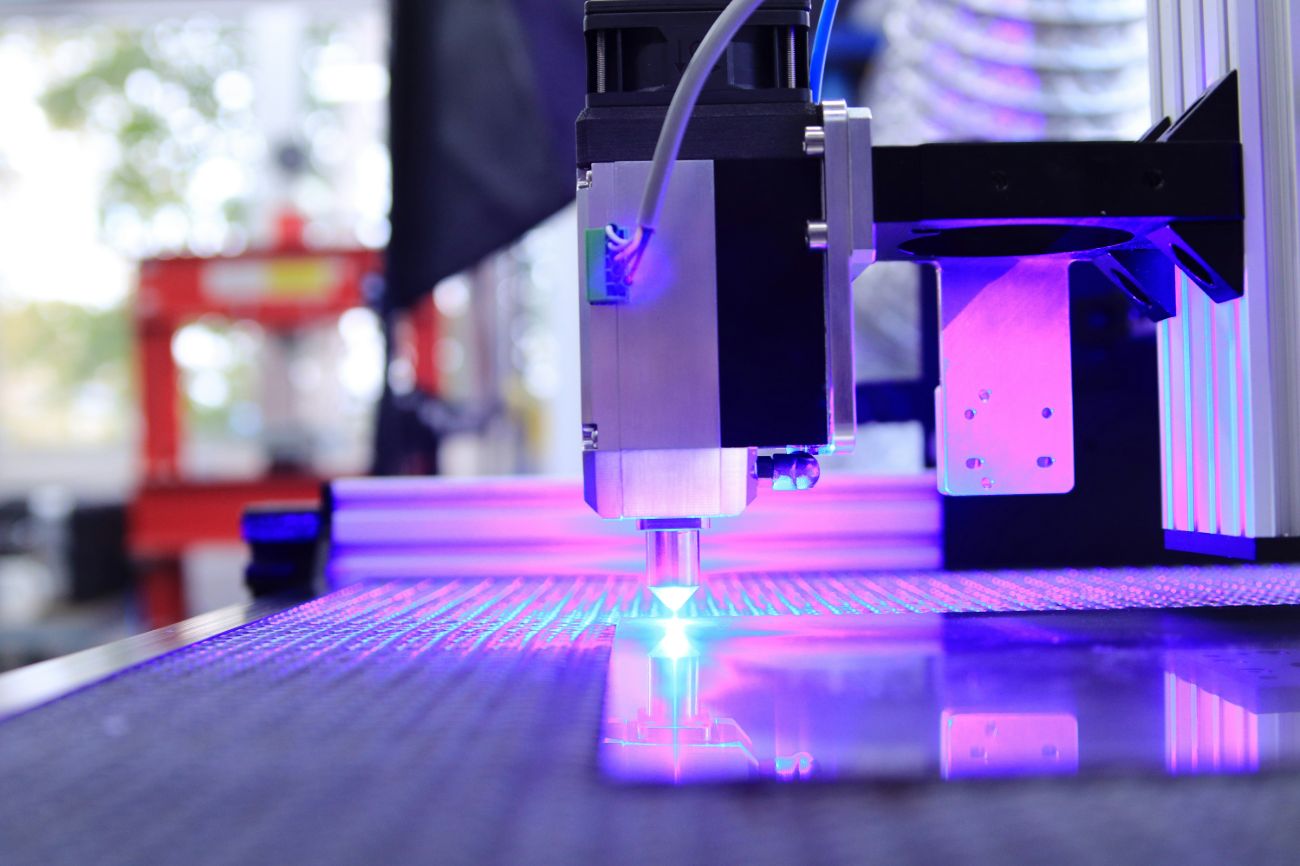
Even a few years ago, 3D printing was just an expensive hobby for lovers. However, thanks to increased competition and development in this field, it has soon become a daily tool for engineers, designers and even ordinary people. This guide will detail everything you need to know about 3D printing and how these machines work.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing It is a way to produce actual 3D objects directly from the computer model. Unlike eliminating something from a large mass, 3D printing creates objects by adding a material in layers. This allows individuals to design spare parts and products of any shape, size and degree of details.
The old 3D printers were slow, expensive, and only a few plastic are used. However, times have changed since then, and devices have become faster, cheaper and more flexible. It is less expensive to create accurate graphics, preliminary models, and small operation without the enormous capital expenses of traditional technologies.
Types of 3D printing techniques
There are many printing techniques, each of which provides unique ways to create objects.
1. FDM codification modeling (FDM)
The most prevalent and used are FDM printers, especially in schools and amateurs. They build things by heating the plastic strands and forcing them on a hot nozzle, and stir the thin plastic layer simultaneously.
2. SLA layout (SLA)
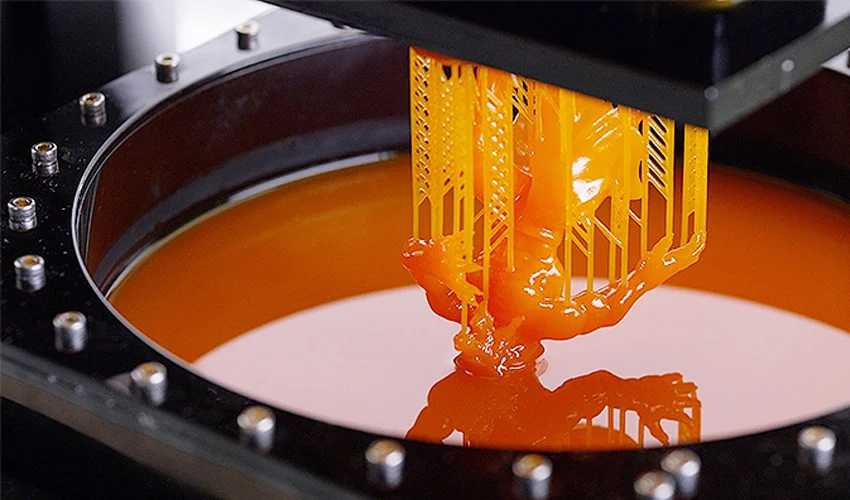
Specifically, SLA Laser printers are used to stiff resin in the plastic called a light time. This method creates parts with very soft surfaces and high accuracy, making it a favorite choice for jewelry, dental models and initial models.
3. SLS (SLS)
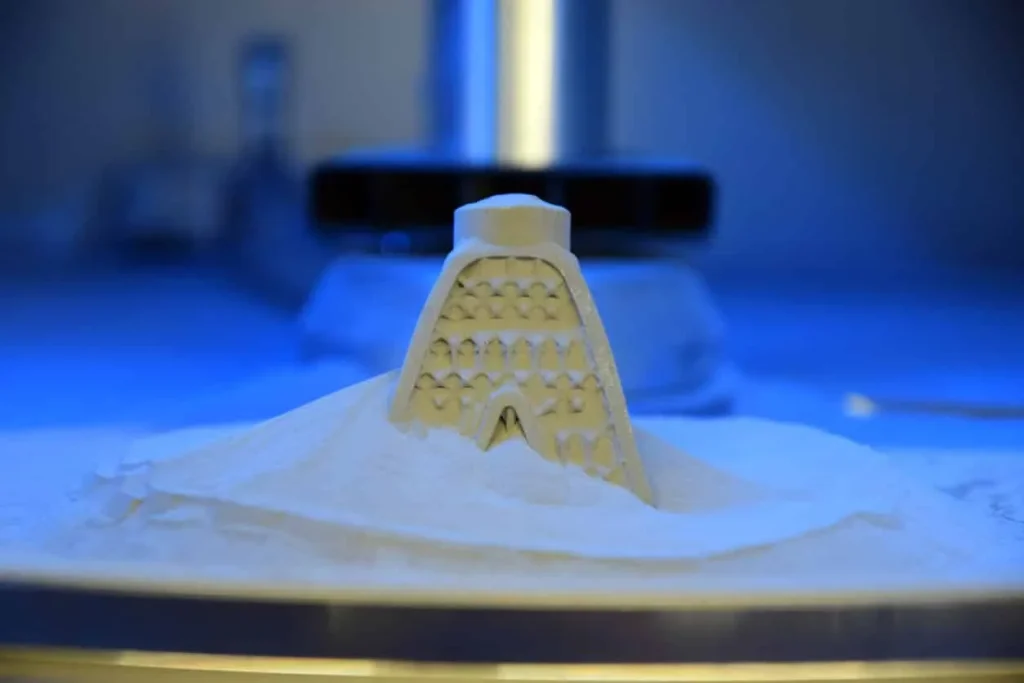
SLS laser printers are used to integrate small amounts of polymer powder into solid ingredients. Since the residue powder works as a support structure for the part while printing, SLS can print dense and detailed parts without further support structures, which are ideal for complex designs.
How does the 3D printer work?
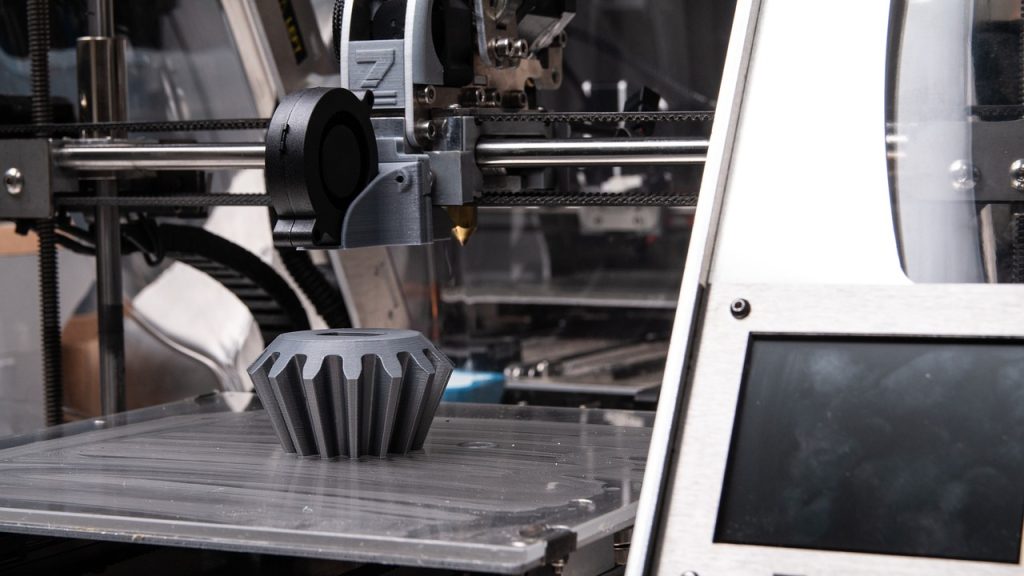

The 3D printer brings a digital idea to life by building a layer of objects carefully. Here’s a simple step by step on how it works:
- Create designDesigners use a specific program called CAD (design with the help of computer) to create a 3D chart for the object. Then the model is exported in a file like StL or OBJ, which can be read by the printer.
- Preparing the form: After that, you download the form to a cutting program. The program cuts the design into thin, horizontal layers and puts the printer guidance, decides the thickness of each layer, the place to add support, and any materials to be used.
- Start printing: Once everything is ready, the file is sent to the 3D printer. The printer implements the instructions of the layer after another. Plastic, liquid resin can be dissolved with laser, or melting and welding powder with heat to gradually build the object.
- Construction: The printer puts one layer at one time. After one layer is complete, the next layer is designed directly on top. In addition, most organisms need a little additional work after finishing printing. This can include washing or processing under UV light, removal of support, sanding, or drawing to improve strength or appearance.
3D printing applications
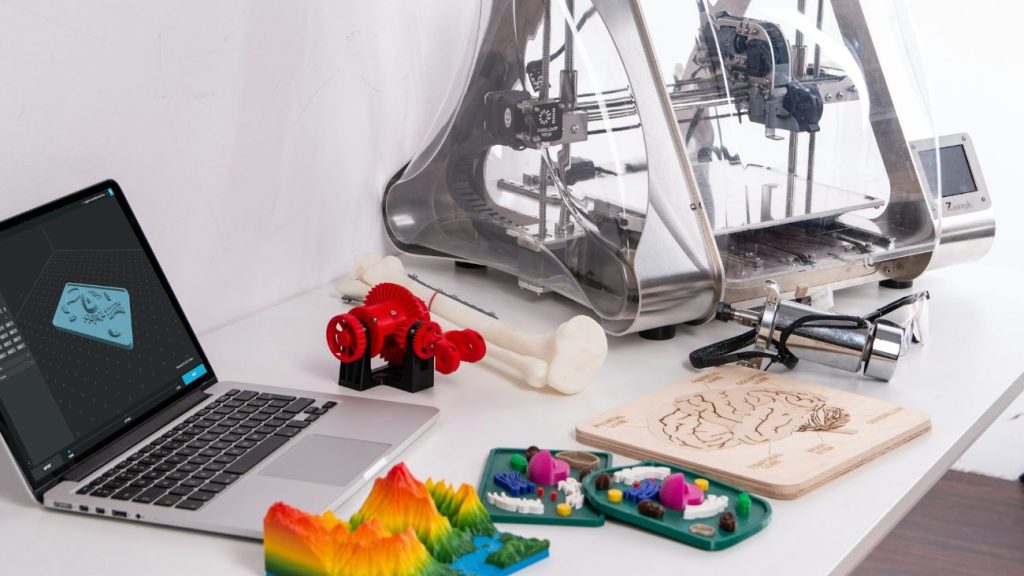

Several 3D printing industries are used to produce goods faster, at lower costs, and with more customization than traditional methods.
- Product design and engineeringDesigners and engineers use 3D printing to quickly translate concepts into 3D reality. It helps them test designs and move faster than concept to the final product.
- manufacturing: The factories use them to produce custom tools, molds and components with reduced costs and faster production without waiting and expensive settings.
- dentistryDentists use 3D printers to produce crowns, bridges, spoils, and more accurate teeth and make faster than traditional methods.
- educationSchools and universities use 3D printers to teach science, engineering and art by allowing students to create real models and learn through practical projects.
- health care: Doctors and medical teams use 3D printing to make patient models, surgical tools, and designated medical devices, and improve care while saving time.
- entertainmentArtists and directors use three -dimensional printing to create statues, costumes, support for movies, TV shows and video games.
- jewelryJewelery makers use 3D printing to design and manufacture custom earrings, rings, molds, and save the time and accuracy needed to carve the hand.
conclusion
Today, three -dimensional printing is no longer the technique of making models only. It provides innovative solutions and improved designs across various fields, including medicine, production and education. Moreover, with new materials and new technologies awaiting the wings, the future of 3D printing appears brighter.