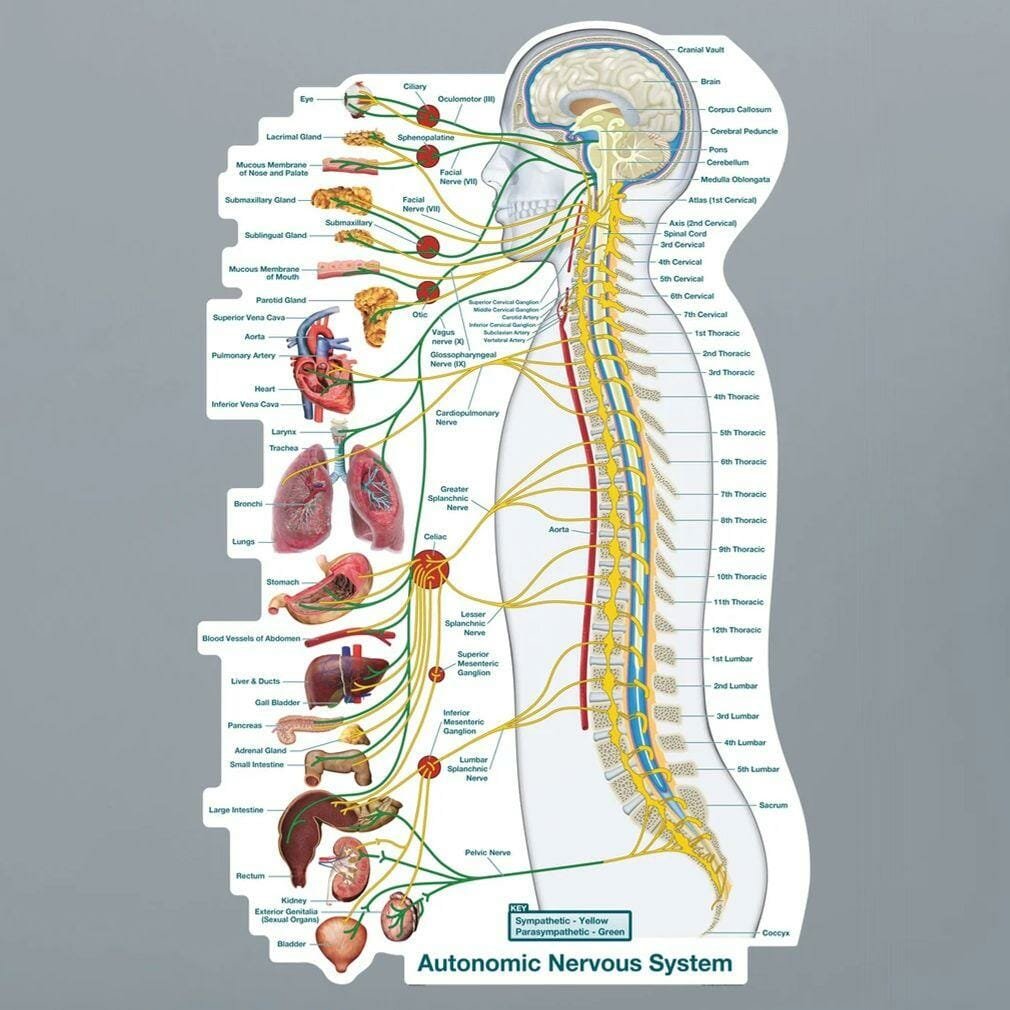
the The involuntary nervous system (ANS) It is a decisive part of the peripheral nervous system that works largely outside our conscious control. The term “independent” stems from Greek words to (Self) and Nomos (Law or Control), which reflects its role in organizing physical functions automatically. It governs non -voluntary physiological processes, including heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, digestion and gland activity. Basically, ASS body managed to maintain internal balance and respond to changes in the internal and external environment without the individual being aware of these modifications.
Involuntary responses are reflexive and emotional. For example, increased heart rate when anxiety, or sweating in response to heat, both are independent functions. These responses are implemented by a complex network of neurons and are decisive to survive and adapt.
Comparison: the physical nervous system against the involuntary nervous system
The human nervous system is divided into Physical nervous system and The involuntary nervous systemEvery special service:
-
Source source:
-
the Physical nervous system In the first place, he is interested in the external environment. It collects sensory information from skin, structural muscles and joints.
-
the The involuntary nervous systemOn the other hand, it monitors internal physical functions. It receives inputs from visceral organs such as the heart, lungs and digestive system.
-
-
Recall website:
-
In the physical system, sensory receptors are located on the surface of the body and inside the musculoskeletal system.
-
In the answer, there are receptors within the organs and interior tissues, such as the stomach, lungs and blood vessels.
-
-
Paths:
-
Sensory nerve cells (factors received) in the physical system enter the spinal cord through Rectal root It usually ends in The dorsal century From the spinal cord.
-
In the answer, the nerve cells also entered through the dorsal root, but they end in Epidem Century (ILH) From the spinal cord, a specialized area for involuntary control.
-
-
Effective paths:
-
the Physical nervous system One kinetic nerve cells are used to connect the central nervous system (CNS) with its goal: structural muscles.
-
the The involuntary nervous system Us a Two Noron series:
-
the Pregninglionic neurons It arises in the body of the brain or spinal cord (specifically in ILH).
-
the A post -harmony nervous cell It is in the involuntary nodes and extends to the target respondent organ (such as smooth muscles or glands).
-
-
-
Effects:
-
Physical neurons that pledge Structural musclesWhich is under voluntary control.
-
InnerVate nerve neurons Small musclesand Heart muscleAnd GlandsAnd they are involuntary effects.
-
ANS divisions: sympathetic to the sample
ANS is divided into two main branches, and each has opposition measures:
The functional effect on the members
Here is how each section affects different systems:
Nervous tankers and receptors in the answer
The involuntary signals depend greatly on the chemical apostles, or Nervous tankersAnd their associated Receptors. Understanding this is very important to gain how different drugs and stimuli affect the involuntary function.
Cholini system (acetylcholine)
-
Pregninglionic neurons In both sympathetic divisions and weaknesses Actill Collin (ACH).
-
Postanglionic parasympathetic nerve cells Also launch anch.
-
This system is referred to as the name ColinIt works on two basic types of receptors:
1. Nicotine receptors
-
It is found in the involuntary nodes, the adrenal gland, and the intersection of the muscle.
-
Activated by nicotine and ACH.
-
Mediation in a rapid interlocking transmission through the ion gate canal.
2. Mascarin receptors
-
It was found in the heart, smooth muscles and glands.
-
It activates the mascers and anch.
-
It has various effects depending on tissues:
-
Heart inhibitors (for example, low heart rate),
-
Excitation in the digestive system system (for example, increased movement and secretion).
-
The Adrenali System (by Norbiniferin)
-
Sympathetic nerve cells after permission The first launch Bafran (Nurradrenaline).
-
This nervous carrier works on Adrenal receptorsWhich was classified as follows:
-
the AdrenalIt is considered a sympathetic node to modify, and the versions Ebenifrin (adrenaline) In the bloodstream, enhance the sympathetic response.
conclusion
the The involuntary nervous system It is a miracle of biological engineering, and it runs smoothly the involuntary activities that keep us alive and in response to our environment. Its branches – sympathetic and helpful – scream at an accurate balance between excitement and relaxation, ensuring that the body is always ready to work or heal. Understanding how to operate these systems not only illuminate the complexities of human physiology, but also constitute the basis for many medical treatments that target cardiovascular, digestive and psychological system disorders.
As we continue to explore AS, its effect on emotional health, the regulation of stress, and even increasingly clear immune responses becomes clear. This complex network really embodies the amazing body’s ability to adapt, protect and preserve itself – without knowing it.